Page 2 - Vol0_No04_2018
P. 2
Lin, Zheng, Shen, Zheng, and Wu: Survey and Analysis of Current State of Ventilator Alarms in the Intensive Care Unit
MATERIALS AND METHOD intervention measures, and alarm causes. Since alarm
Based on the literature review and our experience, limit settings are highly relevant with alarm occurrence,
alarms can be categorized into meaningful alarms and it is also important to record common alarm limit values
meaningless alarms. Meaningful alarms are those alarms accurately. Based on the key elements mentioned above,
that require a clinician’s quick attendance due to changes we design the Statistics of Clinical Meaningful Alarms, as
in patient condition or those technical alarms originating shown in Table 1.
from equipment malfunctions that require timely cor- In this study, we selected the SLE5000 ventilator as an
rection. Meaningless alarms are those that don’t reflect example, where this paper applies the designed survey
the true changes of a patient’s condition, do not improve table to the collection and observation of the SLE5000
patient management, and may be caused by false alarm, ventilator alarms generated in daily use in the neonatal
improper alarm settings, or recoverable transient artifacts. intensive care unit (NICU) over a period of 10 days.
In order to carry out an assessment of the common
ventilator alarms, we first consulted with clinicians to cat- RESULT
egorize the three main alarm interventions for ventilators in The Results of the Survey
their routine practice: (1) clinician’s medical intervention,
This survey is based on 120 total questionnaires, with
(2) clinical engineering and nurse’s equipment correction;
486 events of recorded alarm information from 112 valid
and (3) alarm elimination by silencing. Clinician’s medi-
questionnaires, and 12 kinds of common alarms generated.
cal intervention means patients with clinically changed
The specific number of alarms shown in Figure 1. Among
conditions requiring timely intervention of medical staff;
them, the high-pressure alarm, low pressure alarm, and
clinical engineering and nurse’s equipment correction
cycle failure occur with higher frequency. The results of
means a technical problems with the ventilator occurred
intervention are shown in Table 2.
requiring clinical engineering or nurse’s action such as
According to the effectiveness of the alarm and the
immediate repair; while alarm elimination by silencing
definition of meaningful alarms described earlier, we
means that both the patient and instrument were OK and
classify 354 alarms events as meaningful alarms, and the
the alarm did not recur after silencing. We also collected
calculation of meaningful alarms rate per day is shown
and analyzed common alarm contents, common alarm
in Table 3.
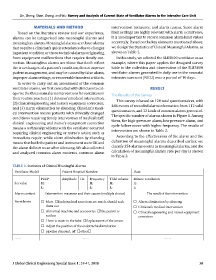
Table 1. Statistics of Clinical Meaningful Alarms
Ventilator Model: Patient Hospital Number: Date:
PEEP Amplitude Hz Frequency Tidal volume Minute ventilation
Set value H: H: H: H:
L: L: L: L:
Alarm content Intervention measures and their causes (multiple choice) The result of the intervention
Event hints: Mute Endotracheal secretions are much, should suck Alarm elimination by silencing
them out Clinician’s medical intervention
Abnormal machine and accessories The patient is Clinical engineering and nurse’s equipment
restless correction
There is water in the tube Replacement of the sensor
Adjust the position of the endotracheal intubation
pipeline discount, off other
…… …… ……
J Global Clinical Engineering Special Issue 1: 37-41; 2018 38